SCEptRe: Structural Complexes of Epitope Receptor - Tutorial
SCEptRe provides weekly updated, non-redundant, user customized benchmark datasets with information on the immune receptor features for receptor-specific epitope predictions. This tool extracts weekly updated 3D complexes of antibody-antigen, TCR-pMHC and MHC-ligand from the Immune Epitope Database (IEDB) and clusters them based on antigens, receptors and epitopes to generate benchmark datasets. Users can customize structural quality and clustering parameters (e.g. resolution, R free factors, antigen or epitope sequence identity) to generate these datasets based on their need.
Antibody-antigen complexes
SCEptRe filters all the 3D antibody-antigen complexes from the IEDB based on structural quality and antigen length parameters provided by the users and then clusters the filtered complexes based on antigen sequence identity, antibody CDR sequence identity and epitope 3D conformation.
The screenshot below illustrates the necessary steps to generate datasets. And more details of each of the steps are described as well as the recommended values of the parameters.
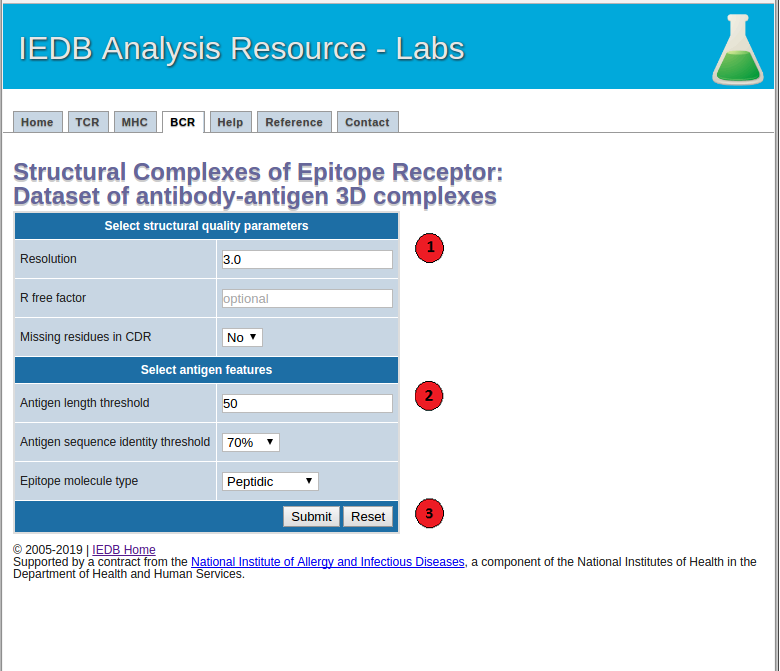
1. Select structural quality parameters.
Resolution: Resolution is a measure of the quality of the crystal structures. Better quality structures have lower resolution values such as 1 Angstrom. More details on the resolution can be found here.
R-free factor: R-free factor is a measure of the quality of the atomic model obtained from the crystallographic data. A random set of atoms will give an R-value of about 0.63, whereas a perfect fit would give a value of 0. Typical R-factor values are about 0.20. More details on the R-free factors can be found here.
Missing residues in CDRs: Most structures do not include coordinates of all the atoms in the molecule. Using this option users can choose whether to allow or not to allow antibody-antigen complexes with missing residues in the CDR regions in the final dataset. More information on the missing atoms in the structures can be found here.
2. Select antigen features.
Antigen length: Users can choose to filter antibody-antigen complexes below the specified antigen length threshold.
Antigen sequence identity threshold: Users can specify an antigen sequence identity threshold to cluster antibody-antigen complexes.
Epitope molecule type: Using this option users can get a list of all the filtered antibody-antigen complexes with peptidic or non-peptidic epitopes. Please note that only the antibody-antigen complexes with peptidic epitopes will be clustered based on their antigen sequence, antibody CDR sequences and epitope conformation. The complexes with non-peptidic epitopes will be filtered based on the specified structural quality parameters and clustered based on their antibody sequences.
3.Submit the prediction.
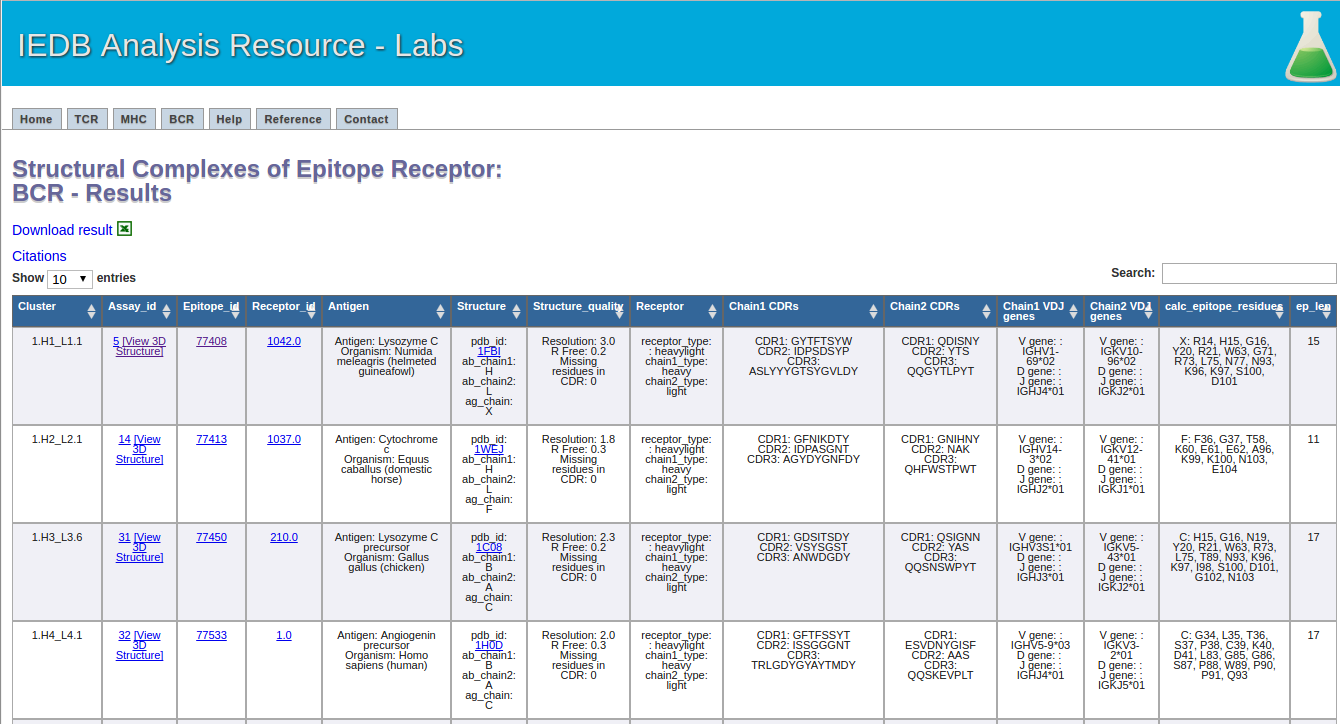
This one is easy. Click the submit button, and a result screen similar to the one below should appear.
4.The recommended parameters for clustering antibody-antigen complexes.
Resolution: 3 Angstrom or lower
Missing residues in CDRs: No
Antigen length: 50 residues or longer
Antigen sequence identity threshold: 70%
TCR-pMHC complexes
SCEptRe filters the 3D TCR-pMHC complexes from the IEDB based on structural quality and epitope length parameters before clustering them based on epitope sequence identity, TCR CDR sequence identity and MHC groove domain (G domain).
The screenshot below illustrates the necessary steps to generate datasets. And more details of each of the steps are described as well as the recommended values of the parameters.
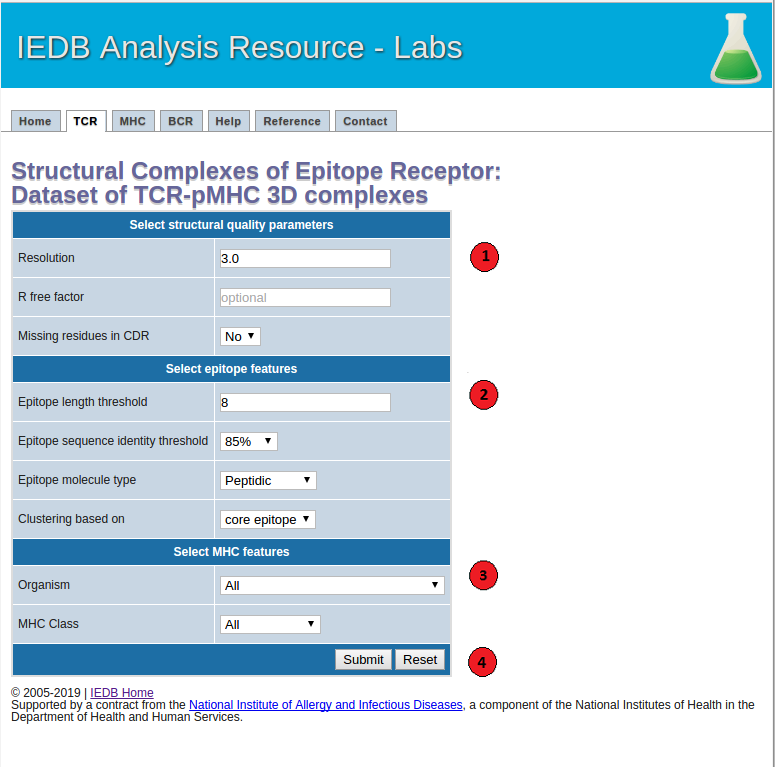
1. Select structural quality parameters.
Resolution: Resolution is a measure of the quality of the crystal structures. Better quality structures have lower resolution values such as 1 Angstrom. More details on the resolution can be found here.
R-free factor: R-free factor is a measure of the quality of the atomic model obtained from the crystallographic data. A random set of atoms will give an R-value of about 0.63, whereas a perfect fit would give a value of 0. Typical R-factor values are about 0.20. More details on the R-free factors can be found here.
Missing residues in CDRs: Most structures do not include coordinates of all the atoms in the molecule. Using this option users can choose whether to allow or not to allow antibody-antigen complexes with missing residues in the CDR regions in the final dataset. More information on the missing atoms in the structures can be found here.
2. Select epitope features.
Epitope length: Users can choose to filter out the TCR-pMHC complexes below the specified epitope length threshold.
Epitope sequence identity threshold: Users can specify an epitope sequence identity threshold to cluster TCR-pMHC complexes.
Epitope molecule type: Using this option users can get a list of all the filtered TCR-pMHC complexes with peptidic or non-peptidic epitopes. Please note that only the TCR-pMHC complexes with peptidic epitopes will be clustered based on their epitope sequence, TCR CDR sequences and MHC G-domains. The complexes with non-peptidic epitopes will be filtered based on the specified structural quality parameters and clustered based on their TCR CDR sequences and MHC G-domains.
Epitope clustering based on: Users can choose to cluster TCR-pMHC complexes based on their core-epitope or whole epitope sequences. Core-epitopes are defined as the peptide residues in direct contact (<=4 Angstrom) with the TCR and MHC molecules.
3. Select MHC features.
MHC organism:: Users can filter the TCR-pMHC complexes based on a MHC source organism.
MHC class: Users can also filter the complexes based on a class I or II of the MHC molecule.
4.Submit the prediction.
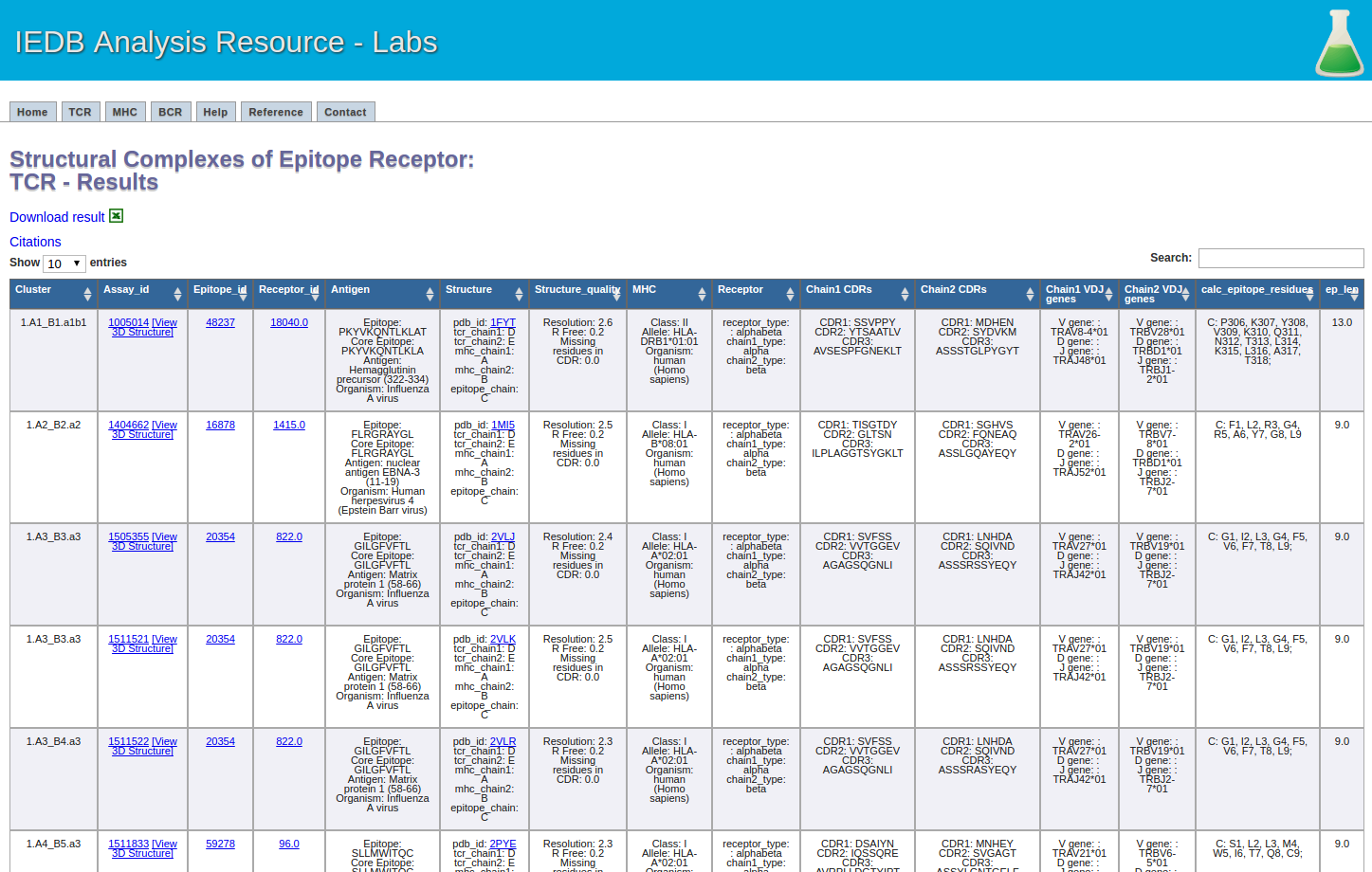
This one is easy. Click the submit button, and a result screen similar to the one below should appear.
5.The recommended parameters for clustering TCR-pMHC complexes.
Resolution: 3 Angstrom or lower
Missing residues in CDRs: No
Epitope length: 8 residues or longer
Epitope sequence identity threshold: 85%
Epitope clustering based on: core-epitope
MHC-ligand complexes
The MHC-ligand complexes from the IEDB are filtered based on structural quality and epitope length parameters and clustered based on epitope sequence identity and MHC G domains.
The screenshot below illustrates the necessary steps to generate datasets. And more details of each of the steps are described as well as the recommended values of the parameters.
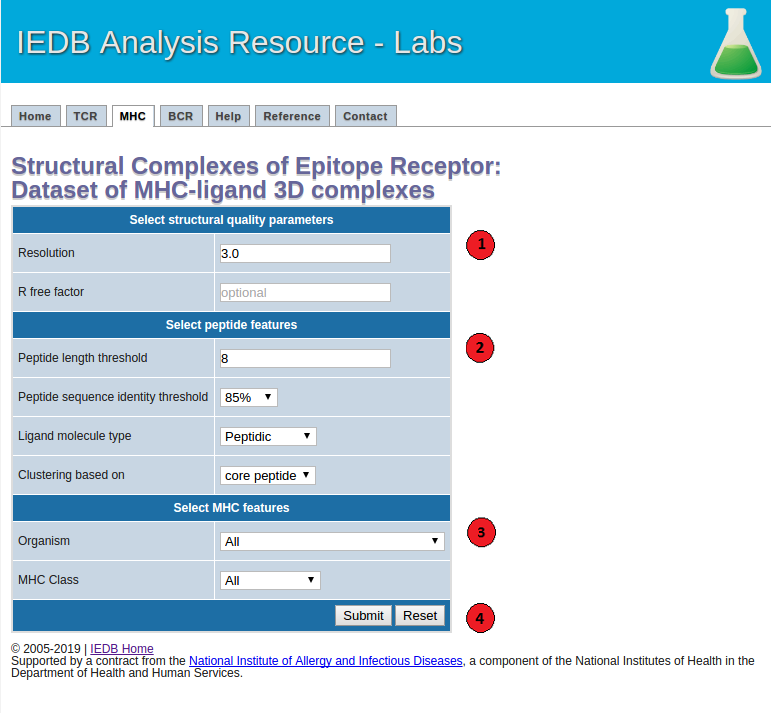
1. Select structural quality parameters.
Resolution: Resolution is a measure of the quality of the crystal structures. Better quality structures have lower resolution values such as 1 Angstrom. More details on the resolution can be found here.
R-free factor: R-free factor is a measure of the quality of the atomic model obtained from the crystallographic data. A random set of atoms will give an R-value of about 0.63, whereas a perfect fit would give a value of 0. Typical R-factor values are about 0.20. More details on the R-free factors can be found here.
2. Select peptide features.
Peptide length: Users can choose to filter out the MHC-ligand complexes below the specified epitope length threshold.
Peptide sequence identity threshold: Users can specify an epitope sequence identity threshold to cluster MHC-ligand complexes.
Ligand molecule type: Using this option users can get a list of all the filtered MHC-ligand complexes with peptidic or non-peptidic ligands. Please note that only the MHC-ligand complexes with peptidic epitopes will be clustered based on their peptide sequences and MHC G-domains. The complexes with non-peptidic ligands will be filtered based on the specified structural quality parameters and clustered based on their MHC G-domains.
Peptide clustering based on: Users can choose to cluster MHC-ligand complexes based on their core-peptide or whole peptide sequences. Core-peptides are defined as the peptide residues in direct contact (<=4 Angstrom) with the MHC molecules.
3. Select MHC features.
MHC organism: Users can filter the MHC-ligand complexes based on a MHC source organism.
MHC class: Users can also filter the MHC-ligand complexes based on a class I or II of the MHC molecule.
4.Submit the prediction.
This one is easy. Click the submit button, and a result screen similar to the one below should appear.
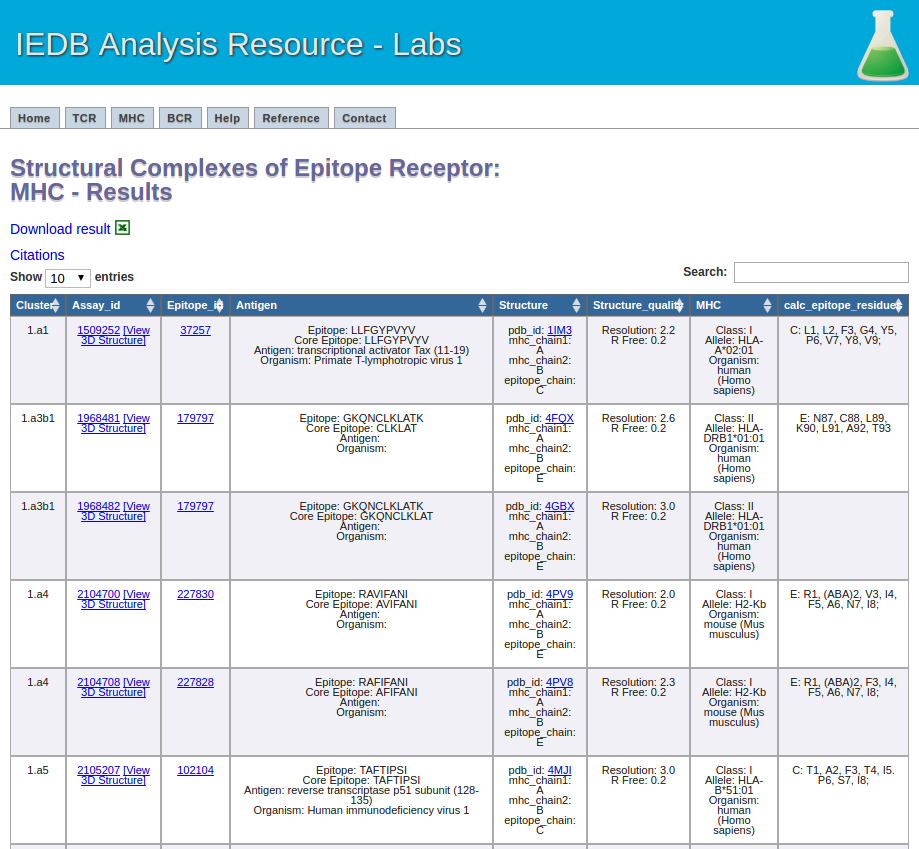
5.The recommended parameters for clustering MHC-ligand complexes.
Resolution: 3 Angstrom or lower
Peptide length: 8 residues or longer
Peptide sequence identity threshold: 85%
Peptide clustering based on: core-peptide
